Taking a closer look at LHC
|
"If there's one thing to do, it's to engage in education". George Charpak (Nobel Prize in Physics in 1992). |
|
CERN celebrates 70 years of scientific discovery and innovation.
Large Hadron Collider is the world’s highest energy particle accelerator. LHC (situated in the northwest suburbs of Geneva on the Franco–Swiss border) generates the greatest amount of information that has ever been produced in an experiment before. It is aimed to reveling some of the most fundamental secrets of nature.

Despite the enormous amount of information available about this topic, it is not easy for non-specialists to know where the data come from.
Basically, the purpose of this Website is to help introducing and informing the wider public about the LHC experiment, and some simple physical calculations which take place in all particle accelerators. They can also be used in secondary school classrooms in order to stimulate the curiosity of the students, help them understand the physical concepts of LHC, and they can also be used as an example of the relationship between the cold equations of Physics on the blackboard and the exciting scientific research.
It is important to point out that the calculations that appear on this website are adapted to secondary school level, and in most cases, although they may be useful, they are simply approximations of the correct results.
We also present below the most recent news on particle physics produced at CERN. In the News section section you will find news from previous years.
We show below some facts that are of special relevance, appearing in the different Sections of this website the development of the concepts and contents that we consider to be of interest.
If you are not familiar with the basic concepts of particle physics, we recommend that you first visit the different sections of the general menu of our website.
We also present below the most recent news on particle physics produced at CERN. In the More News section you will find news from previous years.ite.
CERN highlights in 2023
Taken from CERN WEBSITE
Run 3
Year 2022, starts LHC Run 3 after a vast programme of works completed during Long Shutdown 2 (LS2). Protons collide at higher energies (13.6 TeV compared to 13 TeV) and with higher luminosities (containing up to 1.8 × 1011 protons per bunch compared to 1.3–1.4 × 1011 ) than in Run 2.
This third experimental phase runs until the end of 2025.
A few weeks after the start of RUN3, several records were already reached.
Some of these are:
.- energy with Pb ions: 6.8 Z TeV (or 2.76 TeV/nucleon)
.- peak luminosity: 2.5·1034
.- pile-up (almost simultaneous collision points) > 100
.- stored energy per beam: ~ 400 MJ
Current schedule foresees Long Shutdown 3 (LS3) to start in 2026, one year later than in the previous schedule, and to last for three instead of 2.5 years (taken from CERN Courier).
Energy
In 2012 protons at LHC were running with a beam energy of 4 TeV per proton (8 TeV in collision). At the beginning of 2013, the LHC collided protons with lead ions before going into a long maintenance stop (LS1) until the end of 2014. Running was resumed in 2015 with increased collision 6,5 TeV per proton (13 TeV in collision) and another increase in luminosity. Its maximum total energy of 14 TeV is very close, and after the Long Shutdown 2 (LS2) (2019-2022), in Run 3, an energy of 6,8 TeV per proton (13,6 TeV in collision) has been already reached (very close to the designed maximum initial energy, 7 TeV per proton)
Higgs Boson
One of its main goal has already been achieved in the first phase of operation: to find the Higgs boson.
The Nobel prize in Physics 2013 was awarded to François Englert and Peter W. Higgs "for the theoretical discovery of a mechanism that contributes to our understanding of the origin of mass of subatomic particles, and which recently was confirmed through the discovery of the predicted fundamental particle, by the ATLAS and CMS experiments at CERN's Large Hadron Collider."
The ATLAS and CMS collaborations announced their discovery of the particle at CERN on 4 July 2012. This result was further elucidated in 2013.

Candidate Higgs Decay to four muons recorded by ATLAS in 2012 (Image: ATLAS/CERN).
Interesting articles about the Higgs Boson on the tenth anniversary of its discovery are the following:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.
|
Precisely on the tenth anniversary of the Higgs Boson discovery, it is a good time to point out that research in Particle Physics is as necessary as it has always been. In this respect, the following article in the journal Nature is highly recommendable Particle physics isn’t going to die — even if the LHC finds no new particles Nature. 2022 Jul;607(7917):7-8. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-01819-4. |
The CMS collaboration presented the most precise measurement of the effective leptonic electroweak mixing angle.
April, 2024.
The CMS collaboration presented (2024 Rencontres de Moriond conference) the most precise measurement of the effective leptonic electroweak mixing angle performed at a hadron collider to date, in good agreement with the prediction from the Standard Model.
 The electroweak mixing angle is a key element of these consistency checks. It is a fundamental parameter of the Standard Model, determining how the unified electroweak interaction gave rise to the electromagnetic and weak interactions through a process known as electroweak symmetry breaking. At the same time, it mathematically ties together the masses of the W and Z bosons that transmit the weak interaction. So, measurements of the W, the Z or the mixing angle provide a good experimental cross-check of the Model.
The electroweak mixing angle is a key element of these consistency checks. It is a fundamental parameter of the Standard Model, determining how the unified electroweak interaction gave rise to the electromagnetic and weak interactions through a process known as electroweak symmetry breaking. At the same time, it mathematically ties together the masses of the W and Z bosons that transmit the weak interaction. So, measurements of the W, the Z or the mixing angle provide a good experimental cross-check of the Model.
Measurement of the W-boson mass and width (Γ𝑊) with the ATLAS detector.
April 2024.
Proton-proton data recorded by the ATLAS detector in 2011, at a centre-of-mass energy of 7 TeV, have been used for an improved determination of the W-boson mass and a first measurement of the W-boson width at the LHC.
A particle's width is directly related to its lifetime and describes how it decays to other particles. If the W boson decays in unexpected ways, such as into yet-to-be-discovered new particles, these will influence the measured width.
Using proton-proton collision data at an energy of 7 TeV collected during Run 1 of the LHC, ATLAS measured the W-boson width as 2202 ± 47 MeV. This is the most precise measurement to date made by a single experiment, and—while a bit larger—it is consistent with the Standard-Model prediction to within 2.5 standard deviations .
The updated measurement of the W-boson mass is 80367 ± 16 MeV, which improves on and supersedes the previous ATLAS measurement using the same dataset. The measured values of both the mass and the width are consistent with the Standard-Model predictions.
LHCb collab: Measurement of D0− D0 mixing and CP violation in D0➝ K+π− decays.
March, 2024
At a seminar held March 26 at CERN, the LHCb collaboration at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) presented the results of its latest search for matter–antimatter asymmetry in the oscillation of the neutral D meson, which, if found, could help shed light on the mysterious matter–antimatter imbalance in the universe.
D0 mesons oscillations are identified as small changes in the flavour mixture (matter or antimatter) of the D0 mesons as a function of the time at which they decay. The Kπ decay, reported today, is one of the best channels to study this mixing
The results are consistent with previous studies, confirming the matter–antimatter oscillation of the neutral D meson and showing no evidence of CP violation in the oscillation. The findings call for future analyses of this and other decays of the neutral D meson using data from the third run of the LHC and its planned upgrade, the High-Luminosity LHC.
First observation of photons-to-taus in proton-proton collisions by CMS.
March, 2024
The CMS collaboration announces the observation of two photons creating two tau leptons in proton–proton collisions. It is the first time that this process has been seen in proton–proton collisions, which was made possible by using the precise tracking capabilities of the CMS detector.

Candidate event of a process γγ →ττ process in proton–proton collisions.
It is also the most precise measurement of the tau's anomalous magnetic moment and offers a new way to constrain the existence of new physics.
Taken from CMS Collaboration Website
Precise test of lepton flavour universality in W-boson decays into muons and electrons.
March, 2024
ATLAS Collaboration: Precise test of lepton flavour universality in W-boson decays into muons and electrons in pp collisions at √s=13 TeV with the ATLAS detector. (58th Rencontres de Moriond 2024)
A fundamental axiom of the Standard Model is the universality of the couplings of the different generations of leptons to the electroweak gauge bosons. The measurement of the ratio of the decay rate of W bosons to electrons and and muons, R(μ/e), constitutes an important test of this axiom. Using 140 fb−1 of proton–proton collisions recorded with the ATLAS detector at a centre-of-mass energy of 13 TeV, ATLAS Collaboration reported a measurement of this quantity from di-leptonic events where the top quarks decay into a W boson and a bottom quark.

The measured value of R(μ/e) is 0.9995 ± 0.0045 is in agreement with the hypothesis of universal lepton couplings as postulated in the Standard Model. This is the only such measurement from the Large Hadron Collider, so far, and obtains twice the precision of previous measurements in other laboratories.
Observation of the Bc+ →J/ψ J/ψ π+ π0 decay
January, 2024
LHCb Collaboration: The first observation of the Bc+ →J/ψ π+ π0 decay is reported with high significance using proton-proton collision data, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 9 fb−1, collected with the LHCb detector at centre-of-mass energies of 7, 8, and 13 TeV.
The Bc+ (composed of two heavy quarks, b and c) is the heaviest meson that can only decay through the weak interactions, via the decay of one heavy constituent quark. The decay of Bc+ into a J/ψ and a π+π0 pair has never been observed before, mainly because the precise reconstruction of the low-energy π0 meson through its decay into a pair of photons is very challenging in an LHC proton-proton collision environment.

Diagram for the decays of the Bc+ meson into the J/ψ meson and light hadrons
The large number of b-quarks produced in LHC collisions and the excellent detector allows LHCb to study the production, decays and other properties of the Bc+ meson in detail. Since the Bc+ discovery by the CDF experiment at the Tevatron collider (Fermilab-Chicago), 18 new Bc+ decays have been observed (with more than five standard deviations), all of them by LHCb.
An exabyte of disk storage at CERN
September, 2023
CERN disk storage capacity passes the threshold of one million terabytes of disk space
CERN’s data store not only serves LHC physics data, but also the whole spectrum of experiments and services needing online data management.

The first observation of neutrinos at LHC.
August 2023.
While neutrinos are estimated to be some of the most abundant particles in the universe, observing them has so far proved to be highly challenging, as the probability that they will interact with other matter is very low.
Neutrinos are produced very abundantly in proton colliders such as the LHC, however, up to now, these neutrinos had never been directly observed.
The FASER and SND@LHC collaboration are two distinct research efforts, both utilizing the LHC at CERN. Recently, these two efforts independently observed the first collider neutrinos, which could open important new avenues for experimental particle physics research.
ATLAS sets record precision on Higgs boson’s mass.
July 2023.
Taken from CERN Website.
The mass of the Higgs boson is not predicted by the Standard Model and must therefore be determined by experimental measurement. Its value governs the strengths of the interactions of the Higgs boson with the other elementary particles as well as with itself. A precise knowledge of this fundamental parameter is key to accurate theoretical calculations which, in turn, allow physicists to confront their measurements of the Higgs boson’s properties with predictions from the Standard Model. Deviations from these predictions would signal the presence of new or unaccounted-for phenomena.
The new ATLAS measurement combines two results: a new Higgs boson mass measurement based on an analysis of the particle’s decay into two high-energy photons (the “diphoton channel”) and an earlier mass measurement based on a study of its decay into four leptons (the “four-lepton channel”).
The new measurement in the diphoton channel, which combines analyses of the full ATLAS data sets from Runs 1 and 2 of the LHC, resulted in a mass of 125.22 billion electronvolts (GeV) with an uncertainty of only 0.14 GeV (0.09%).
First evidence of the rare decay of the Higgs boson into a Z boson and a photon.
May 2023.
The Standard Model predicts that, if the Higgs boson has a mass of around 125 GeV, approximately 0.15% of Higgs bosons will decay into a Z boson and a photon.
But some theories that extend the Standard Model predict a different decay rate. Measuring the decay rate therefore provides valuable insights into both physics beyond the Standard Model and the nature of the Higgs boson.
In a new study, ATLAS and CMS have now joined forces to maximise the outcome of their search. By combining the data sets collected by both experiments during the second run of the LHC, which took place between 2015 and 2018, the collaborations have significantly increased the statistical precision and reach of their searches.
This collaborative effort resulted in the first evidence of the Higgs boson decay into a Z boson and a photon. The result has a statistical significance of 3.4 standard deviations, which is below the conventional requirement of 5 standard deviations to claim an observation. The measured signal rate is 1.9 standard deviations above the Standard Model prediction.
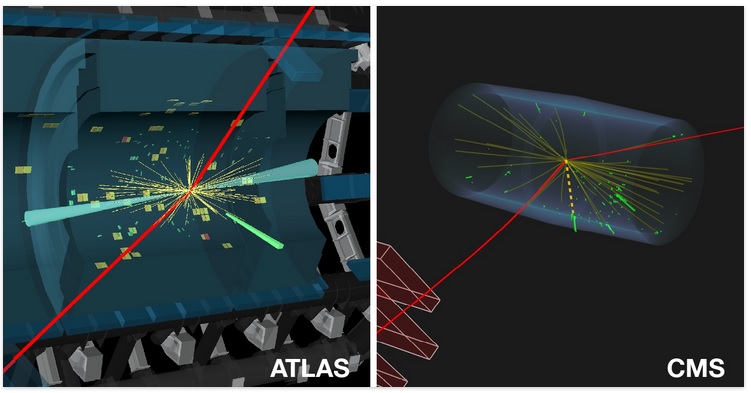
... and to know what is coming see HL-LHC: High Luminosity and also The Future Circular Collider.
CERN Council appoints Fabiola Gianotti for second term of office as CERN Director General (Nov 2019)
At its 195th Session (Nov 2019), the CERN Council selected Fabiola Gianotti, as the Organization’s next Director-General, for her second term of office. Gianotti’s new five-year term of office goes from 1 January 2021 to Decembrer 2025. This is the first time in CERN’s history that a Director-General has been appointed for a full second term.
IMPORTANT NOTICE
For the bibliography used when writing each Section in this Website please go to the References Section
We reiterate that the calculationscalculations that you will be finding in this Website are adapted from the Physics of Secondary School and in most cases they are just very simple approaches to the correct results.
Besides the Sections of this Website, it may be interesting to take a look at other websites which give simple description of Particle Physics. For example: An Introduction To Particle Physics or other ones that you can find in the section Education of this website.
This Website has received the permissión of CERN to use informations, data, texts and images from CERN websites. The use on this Website of the various materials from publications produced by CERN is strictly in accordance with CERN's terms of use.
The rest of images, graphs, etc., not belonging to us, have been taken as "fair use" qualification, but, please, let us know if that is not the case.
A Glossary with an alphabetical list of particle physics terms is included in the last section of this website.
|
AUTHORS Xabier Cid Vidal, PhD in experimental Particle Physics for Santiago University (USC). Research Fellow in experimental Particle Physics at CERN from January 2013 to Decembre 2015. He was until 2022 linked to the Department of Particle Physics of the USC as a "Juan de La Cierva", "Ramon y Cajal" fellow (Spanish Postdoctoral Senior Grants), and Associate Professor. Since 2023 is Senior Lecturer in that Department.(ORCID). Ramon Cid Manzano, until his retirement in 2020 was secondary school Physics Teacher at IES de SAR (Santiago - Spain), and part-time Lecturer (Profesor Asociado) in Faculty of Education at the University of Santiago (Spain). He has a Degree in Physics and in Chemistry, and he is PhD for Santiago University (USC) (ORCID). |
CERN CERN Experimental Physics Department CERN and the Environment |
LHC |
IMPORTANT NOTICE
For the bibliography used when writing this Section please go to the References Section
© Xabier Cid Vidal & Ramon Cid - rcid@lhc-closer.es | SANTIAGO (SPAIN) |








